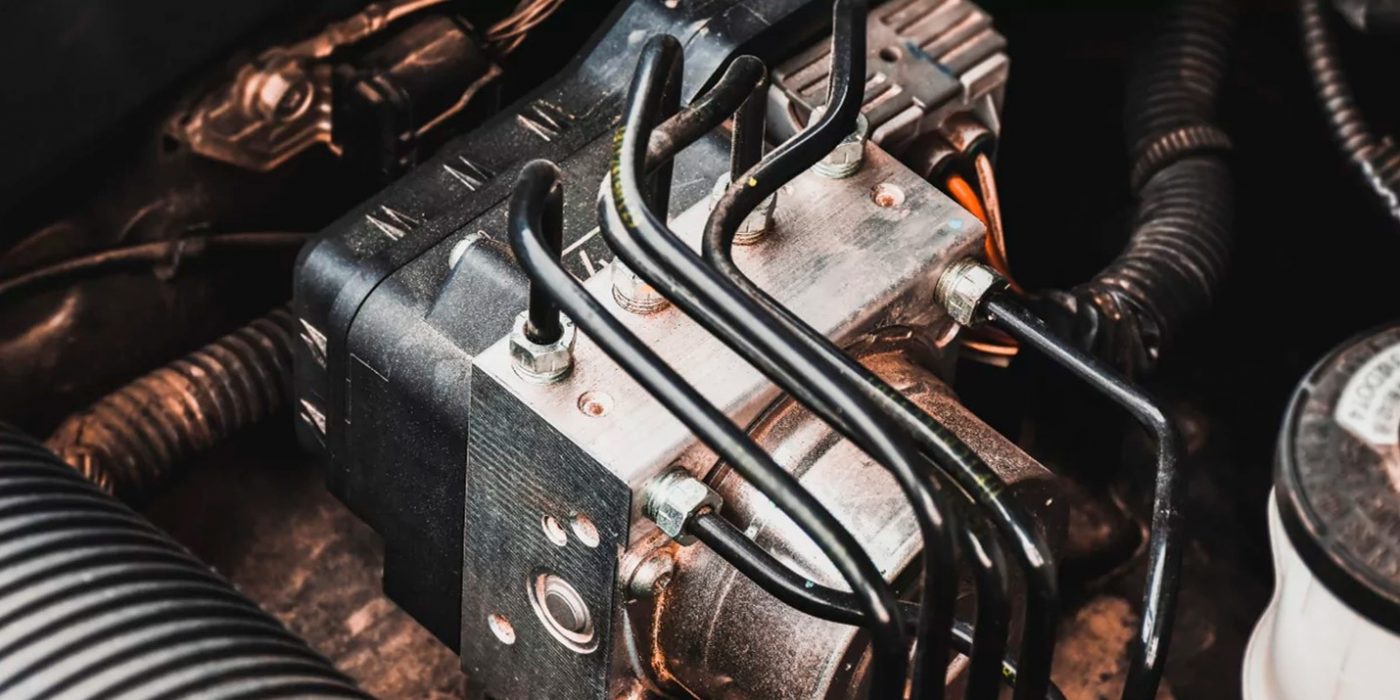
This is part of our series of blog posts designed to help customers understand their vehicle better. Please keep in mind these are general descriptions of how these modules function. There are differences in many years and models, but generally the principles remain the same.
What is an ABS Module & Pump?
The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) module and pump play a crucial role in maintaining vehicle safety during braking, especially in emergency or slippery conditions. Here’s how they work and why they are important:
- ABS Module:
The ABS module is essentially the brain of the Anti-lock Braking System. It monitors and controls the ABS operation using data from various sensors. These sensors detect the wheel speed and feed that information back to the ABS module. If the module detects that one or more wheels are slowing down too much (or locking up), it will activate the ABS system to prevent the wheels from locking.
How the ABS Module Works:
- Sensors: Wheel speed sensors on each wheel continuously monitor the rotation speed of the wheels. If a wheel is about to lock up (i.e., stop rotating while the vehicle is still moving), the system activates.
- Control Logic: The ABS module processes the data from the wheel sensors and decides whether to intervene. The module is programmed to recognize when braking forces are too high, and it will reduce or modulate the braking force to prevent a skid.
- Electronic Control: When the system detects a potential wheel lockup, the module sends signals to the ABS pump and valves to reduce brake pressure, momentarily preventing the wheel from locking. It may rapidly pulse the brake pressure several times per second (this is often felt as a “pulsing” or “vibration” in the brake pedal).
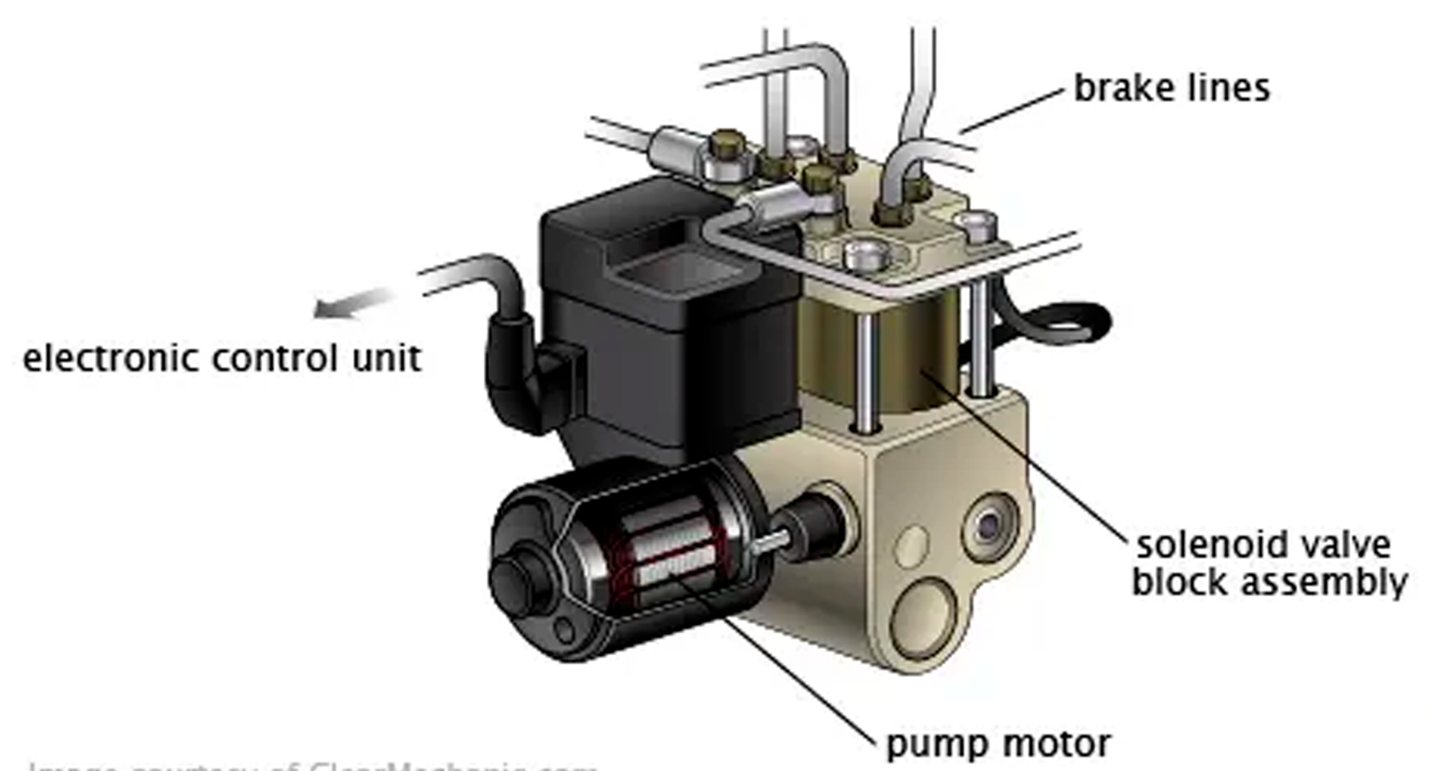
2. ABS Pump:
The ABS pump works in conjunction with the ABS module to control brake fluid pressure during an ABS event (i.e., when the wheels are at risk of locking). The pump is responsible for increasing and maintaining the appropriate pressure in the brake system when needed.
How the ABS Pump Works:
- Pressure Control: When the ABS module determines that a wheel is in danger of locking, it sends a signal to the ABS pump to either reduce or increase the brake fluid pressure. The pump can increase pressure to certain brakes to prevent them from locking, or it can release pressure if the braking force is too strong.
- Hydraulic Valves: The pump works with hydraulic valves that are installed at each wheel brake. These valves open or close based on the commands from the ABS module, allowing the ABS system to control the braking force in each wheel individually.
- Rapid Pulsing: During an ABS intervention, the pump may need to rapidly increase or decrease fluid pressure, which is why you often feel the brake pedal pulsing. This pulsing is the system modulating the pressure to allow the tire to regain traction.
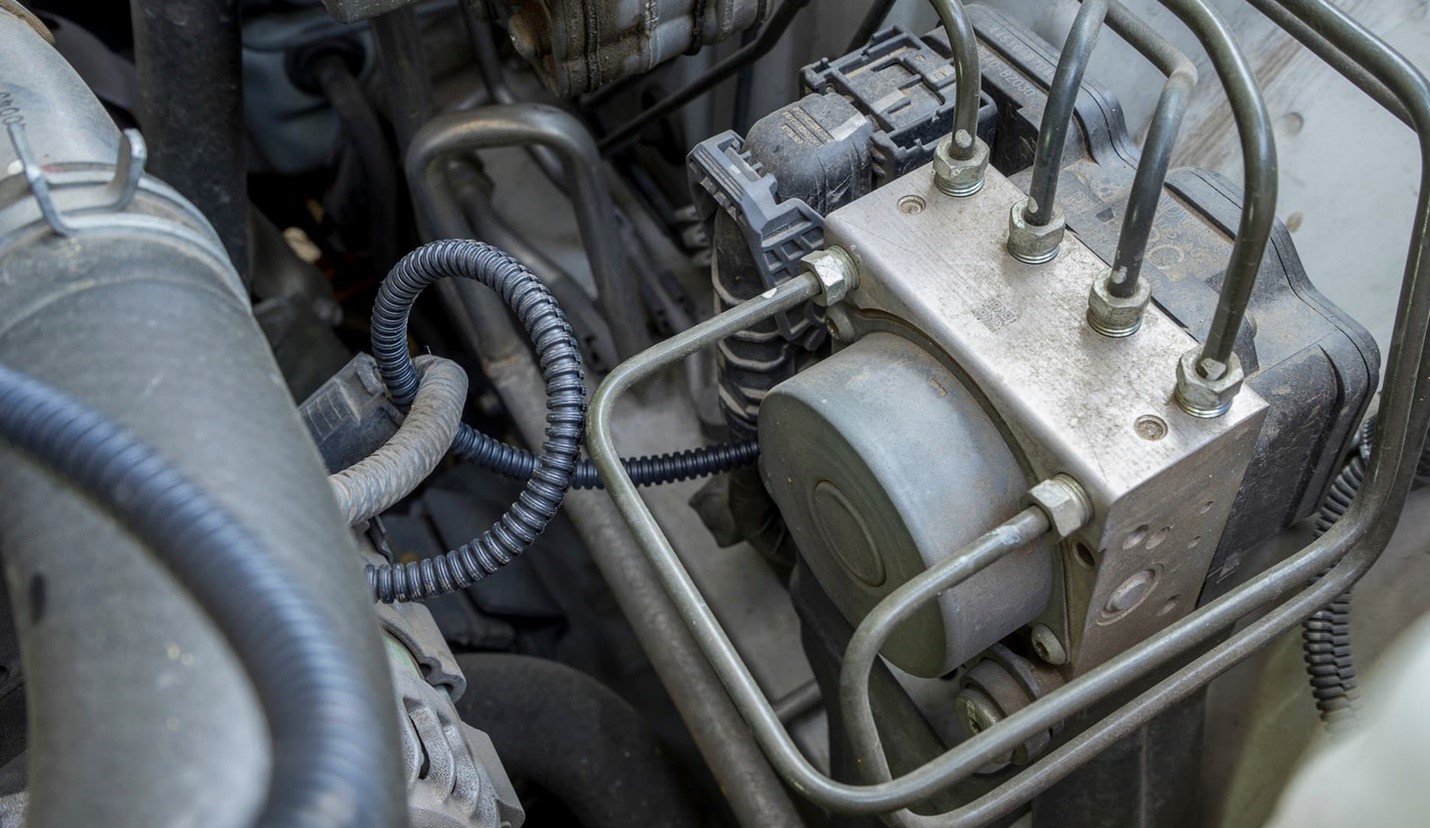

Importance of the ABS Module and Pump Working Properly:
- Prevents Wheel Lockup: The primary function of ABS is to prevent the wheels from locking up during heavy braking. If the wheels lock, the vehicle can skid and lose control. ABS allows the driver to maintain steering control during emergency braking situations.
- Improves Braking Performance in Slippery Conditions: On icy, wet, or gravel roads, ABS is especially beneficial. It helps prevent wheel lockup by adjusting brake pressure quickly, which is crucial for maintaining vehicle stability and control on low-traction surfaces.
- Increases Safety: ABS reduces the risk of losing control of the vehicle during emergency stops, as it helps avoid skidding. This is critical for avoiding accidents, particularly in adverse weather conditions. Without ABS, the driver would be more likely to experience uncontrollable skidding or loss of steering ability.
- Reduces Stopping Distance (Under Certain Conditions): While ABS doesn’t necessarily shorten stopping distance in all conditions (such as on dry, level pavement), it helps to minimize stopping distance in slippery conditions by preventing wheel lockup, which can increase stopping time.
- Helps Prevent Understeering or Oversteering: ABS contributes to better vehicle stability during braking. Without ABS, sudden braking can cause the vehicle to veer left or right (understeer or oversteer) due to wheel lockup, but ABS reduces this tendency by maintaining better control of individual wheels.
Why a properly functioning ABS module & pump is Important:
- Loss of ABS Functionality: If the ABS module or pump fails, the vehicle may still be able to brake normally in most conditions, but you lose the enhanced control and safety that ABS provides. Braking may become less effective in slippery conditions, and you could experience more wheel lockup, increasing the risk of losing control during a panic stop.
- Warning Indicators: Most modern vehicles are equipped with an ABS warning light on the dashboard. If this light comes on, it indicates a problem with the ABS system, such as a malfunction in the ABS module, sensors, or pump. It’s important to address ABS issues promptly because, without it, the vehicle may be harder to control in emergency situations.
In Summary:
The ABS module and ABS pump work together to regulate braking force and prevent wheel lockup, especially in slippery or emergency braking conditions. The ABS system allows for better vehicle control, reduces stopping distance on low-traction surfaces, and increases safety overall. Ensuring that the ABS module and pump are functioning properly is vital for maintaining the effectiveness of your braking system, particularly in emergencies or challenging road conditions. If either component fails, your vehicle may lose these safety benefits, potentially increasing the risk of accidents.
Our next post will delve into the common symptoms of a faulty ABS module.
Visit www.xemodex.com to check out our products and services.
Looking specifically for an ABS module repair service? Check out our ABS services here:
US Customers click here: https://xemodex.com/us/abs-modules/
Canadian Customers click here: https://xemodex.ca/ca/abs-modules/