This is part of our series of blog posts designed to help customers understand their vehicle better. Please keep in mind these are general descriptions of how these modules function. There are differences in many years and models, but generally the principles remain the same.

What Is a Body Control Module? A Simple Guide to One of Your Vehicle’s Most Important Brains
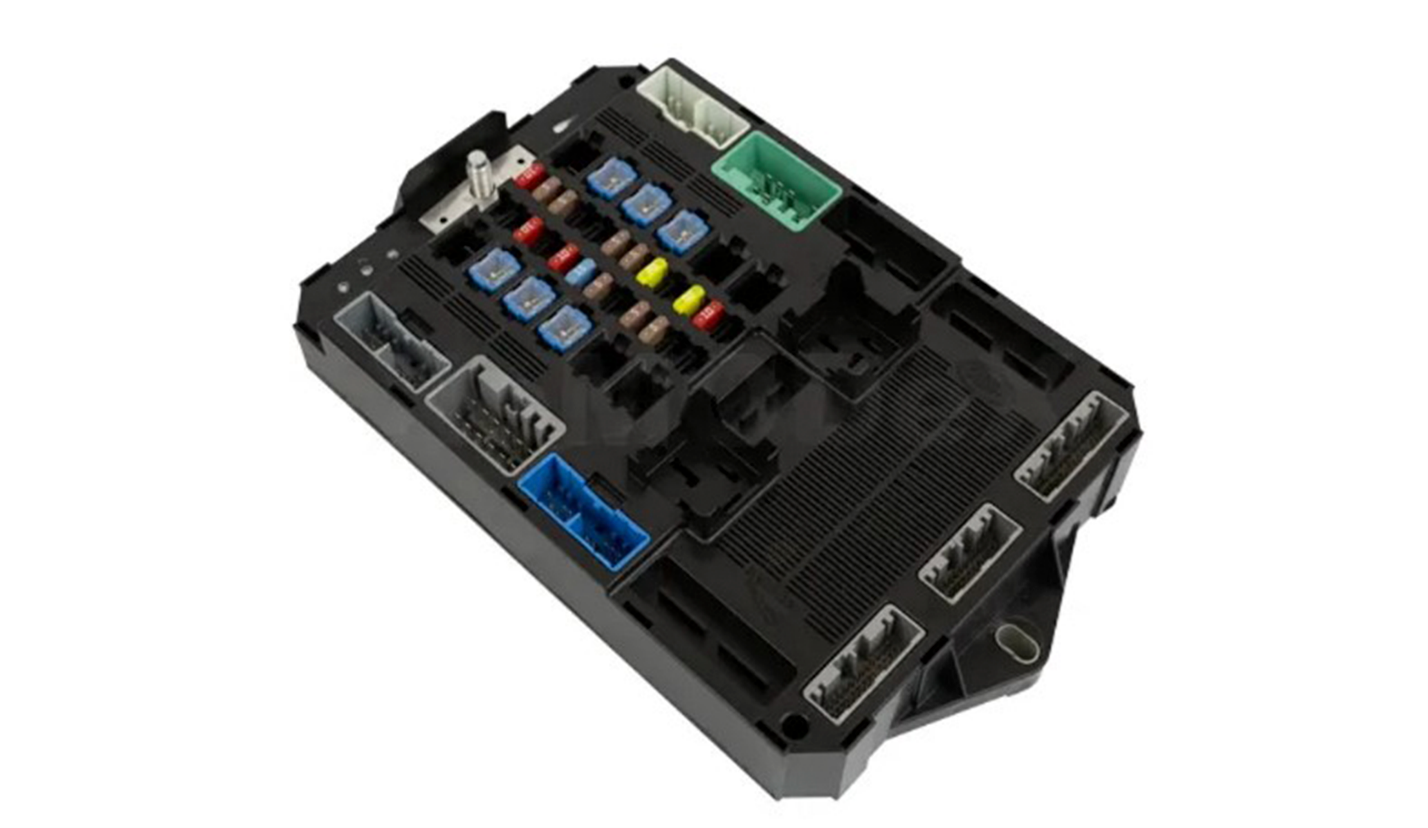
When people think about automotive electronics, they usually picture the engine computer (Engine Control Module), or maybe the infotainment system if they’re currently frustrated with Bluetooth. But hidden behind the scenes is another essential piece of technology that keeps your vehicle’s everyday functions running smoothly: the Body Control Module (BCM).
Note: BCM can also stand for “Brake Control Module”, so remember to be specific when dealing with your mechanic or your customer.
Even though Body Control Modules don’t manage horsepower or fuel delivery, your vehicle would feel pretty lifeless without it. Understanding what a Body Control Module does, how it works, and why it fails can save you time, stress, and money when electrical issues arise.
What Exactly Does a Body Control Module Do?
Think of the BCM as the events coordinator for your vehicle. It controls and monitors dozens of comfort, convenience, and safety functions, including:
- Power door locks
- Interior and exterior lighting
- Wipers and washers
- Power windows
- Alarm system and immobilizer
- Keyless entry and remote start
- HVAC and climate control
- Mirrors, seats, and other “body” features
In modern vehicles, the BCM is also responsible for interpreting signals from switches, sensors, and other modules. It then sends commands across the vehicle’s communication network—often CAN bus or LIN bus—to make sure everything responds correctly.
Because of this, the BCM has become one of the most important electronic modules in today’s cars and trucks.
Why Is the BCM So Important?
Modern vehicles rely on complex networks of interconnected modules. The BCM acts as a communication hub, playing a vital role in everything from security to lighting to power distribution. When it begins to fail, symptoms can range from mildly annoying to completely immobilizing:
- Random lights turning on or off
- Doors locking on their own—or refusing to lock
- Dead power windows
- Wipers that have a mind of their own
- No-crank or no-start conditions
- Battery drain from stuck circuits
- Accessories that stop working intermittently
A future blog post will go into more detail about faults and symptoms of a faulty BCM, but in short, a failing BCM can make the vehicle feel haunted, disobedient, or totally unresponsive.
At XeMODeX, we regularly see BCM failures caused by water intrusion, corroded pins, damaged circuit traces, failed relays, overheating, or simply age-related electronic wear. Since BCMs often house multiple interconnected systems, even a small fault inside the module can create widespread electrical problems.
Different Names, Same Idea: BCMs by Manufacturer
Although most automakers use the term “Body Control Module,” many brands use their own naming conventions or integrate BCM functions into larger electronic units. Understanding these names can make diagnosing electrical issues much easier.
Volvo – Central Electronic Module (CEM)
Volvo vehicles don’t use a traditional BCM. Instead, they rely on a CEM, which controls many body functions and acts as a communication gateway. This makes the CEM one of the most critical modules in any Volvo, and one of the most common repairs we perform at XeMODeX.
Dodge/Chrysler/Jeep/RAM – Totally Integrated Power Module (TIPM)
The well-known TIPM is far more than just a fuse and relay box. It includes integrated microprocessors and control circuits that function like a BCM. TIPM failures can cause fuel pump issues, lighting problems, horn activation, and other erratic electrical behavior.
Ford – Smart Junction Box (SJB)
Ford’s SJB combines the functions of a fuse panel with the intelligence of a BCM. Water intrusion and connector corrosion are frequent troublemakers here.
GM – Body Control Module (BCM)
GM sticks with the traditional name, but these BCMs are heavily integrated into security and lighting circuits. When replaced or repaired, they often require immobilizer relearning and specific programming procedures.
Whether it’s called a BCM, CEM, TIPM, SJB, or Smart Fuse Box, the purpose is the same: controlling the electrical systems that make your vehicle’s “body functions” work properly.
Why BCM Repair Matters
Because the Body Control Module plays such a central role in your vehicle’s electrical system, proper diagnostics and repair are crucial. Many drivers end up replacing switches, relays, or even wiring harnesses unnecessarily because failing BCMs can mimic so many different problems.
At XeMODeX, we specialize in long-lasting module repairs, not temporary fixes. Our technicians use upgraded components, advanced diagnostic tools, and full-scale function testing to ensure each module performs reliably once reinstalled. And if your specific BCM or CEM isn’t listed on our website, you can always submit a Custom Request. We handle hundreds of model variations every year.
The Bottom Line
The Body Control Module might not be the flashiest part of your vehicle, but it’s one of the most essential. It manages the comfort, convenience, and safety features you rely on daily. When a BCM, CEM, TIPM, or SJB starts to fail, the whole vehicle can feel out of sync.
Understanding how these modules work, and why they matter, helps drivers make better repair decisions, avoid unnecessary parts replacements, and get their vehicle back to normal faster.
If you’re experiencing BCM-related symptoms, XeMODeX is here to help with professional diagnostics and long-lasting electronic module repairs.
Visit www.xemodex.com to check out our products and services.