This is part of our series of blog posts designed to help customers understand their vehicle better. Please keep in mind these are general descriptions of how these modules function. There are differences in many years and models, but generally the principles remain the same.
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is a crucial component in any modern automatic transmission system. It communicates with various sensors and the Engine Control Module (ECM) to ensure smooth shifting, proper gear selection, and overall drivability. When the TCM starts to fail, it can lead to a wide range of issues—some obvious, others more subtle. In this post, we’ll explore the most common symptoms of a faulty TCM, some specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and why thorough diagnostics are always essential before replacing or repairing this module.

Common Symptoms of a Failing TCM
1. Erratic Shifting or Harsh Gear Engagement
One of the most noticeable signs of a TCM problem is inconsistent or harsh shifting. This may feel like the vehicle is slamming into gear, especially between 1st and 2nd or when downshifting. In some cases, the vehicle may skip gears, or seem confused about which gear to engage.
2. Failure to Shift or Stuck in a Single Gear
Some vehicles enter a “limp mode” to protect the transmission when the TCM is malfunctioning. This limits the car to second or third gear, preventing normal acceleration and making highway driving difficult or unsafe.
3. Transmission Slipping
If the TCM is failing, it may send incorrect signals to the solenoids, resulting in the transmission slipping out of gear or having difficulty engaging. This can feel like a momentary loss of power, especially during acceleration.
4. Check Engine Light or Transmission Warning Light
Many TCM issues will trigger the Check Engine Light (CEL) or a specific Transmission Warning Light. Retrieving codes from a scan tool is often the first step in diagnosis.

Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to TCM Failure
Depending on the vehicle’s make and model, different codes may appear. Here are a few examples:
• P0700 – General TCM fault. This code often appears alongside other more specific transmission-related codes.
• P0715 – Input/turbine speed sensor circuit malfunction.
• P0720 – Output speed sensor circuit malfunction.
• P0613 – TCM processor fault (often seen in Chrysler and Dodge vehicles).
• U0101 – Lost communication with TCM (common in many GM, Nissan, and Mercedes-Benz models).
Make/Model Variations in TCM Faults and Codes
It’s important to understand that not all vehicles react the same way to a failing TCM. Different automakers use different transmission systems, and even within the same brand, models can vary significantly:
• Volkswagen/Audi vehicles using DSG transmissions may experience hesitation or jerking during shifting, often with P17BF or P17D7 codes.
• Ford vehicles equipped with the PowerShift transmission are known for shuddering and hesitation, sometimes related to TCM faults triggering P090C, P0919, or U0401.
• Mercedes-Benz vehicles with 722.6 or 722.9 transmissions may go into limp mode and show P0717 or U0101.
• GM vehicles might set P0700 along with transmission-specific codes if the TCM is losing communication or failing to properly regulate pressure.
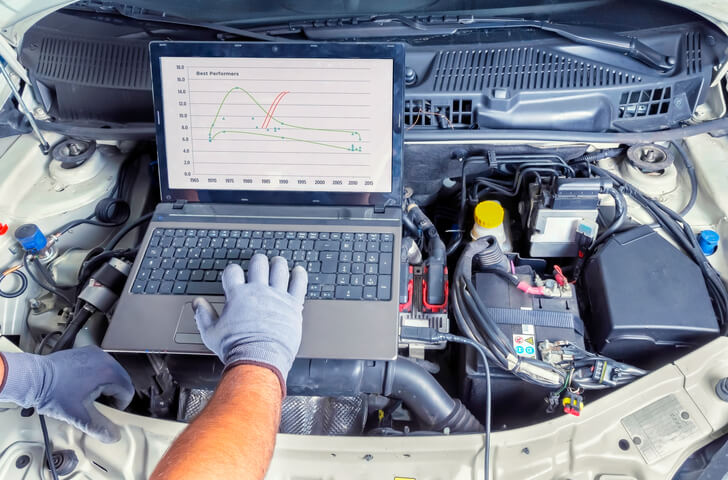

Why Thorough Diagnostics Are Essential
While TCM failure is a serious issue, it’s not always the root cause of transmission problems. Transmission systems are made up of numerous components: solenoids, sensors, valve bodies, wiring harnesses, and more. A faulty speed sensor or corroded wiring can mimic TCM failure, so it’s vital to perform a complete diagnostic scan, inspect wiring, and confirm power and ground supply to the module before assuming the TCM is the culprit.
Visit www.xemodex.com to see our products and service.