Body:
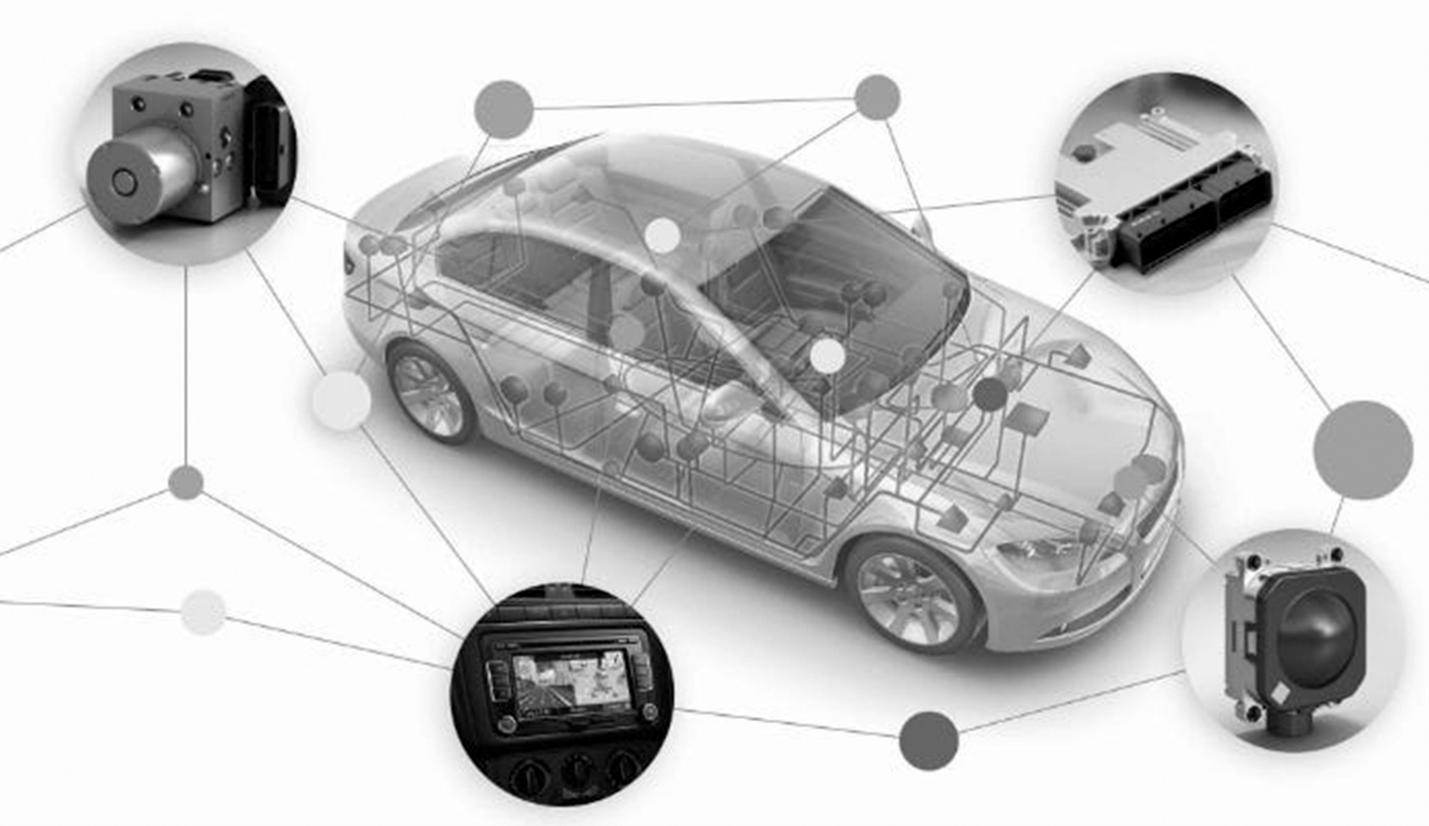
The Controller Area Network (CAN) is the backbone of modern vehicle electronics, allowing different modules and components to communicate efficiently. Nearly every vehicle on the road today relies on a CAN network for vital operations, making a deep understanding of this technology crucial for effective diagnostics and repairs.
What is a CAN Network?
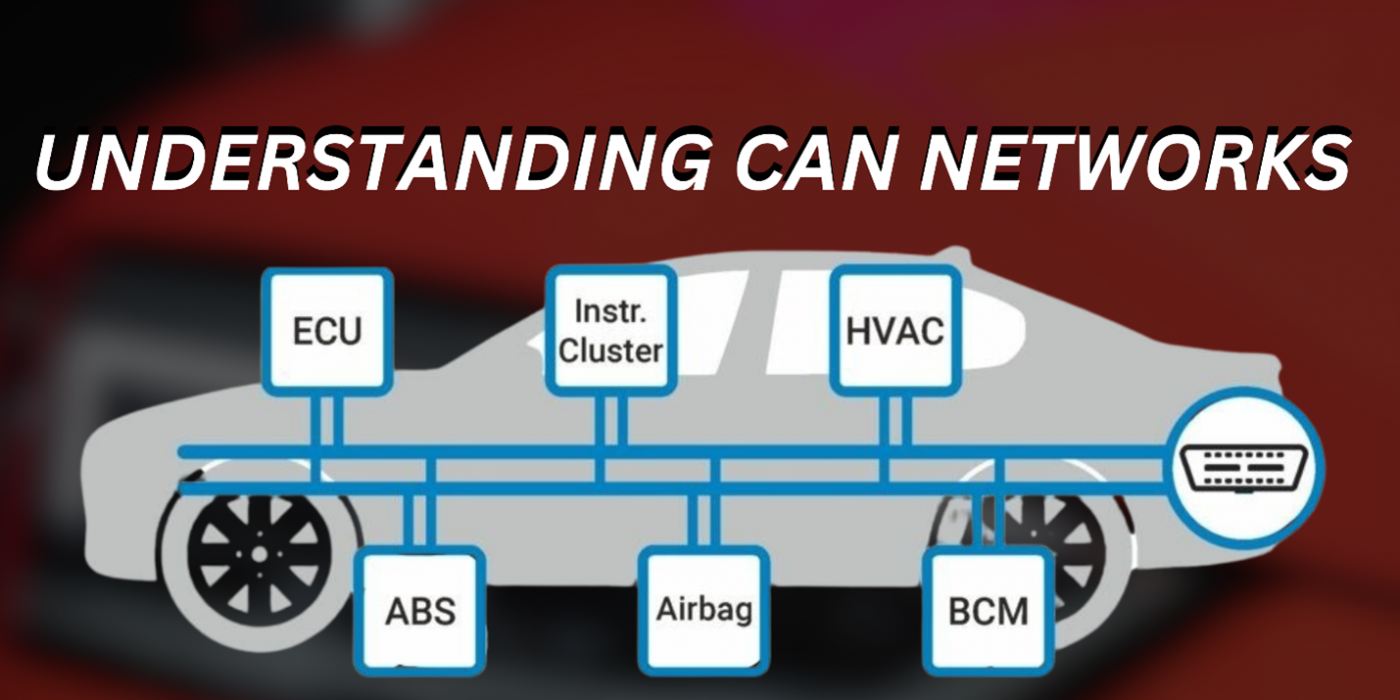
A CAN network is a robust communication system that enables electronic control units (ECUs) to exchange information without the need for a central computer. Instead of each module requiring a direct connection to others, they share a common communication bus, drastically reducing wiring complexity and improving system reliability. CAN networks use two dedicated wires—CAN High and CAN Low—to transmit data between modules.
How CAN Networks are Used in Vehicles
Modern vehicles contain numerous modules controlling essential functions such as engine performance, transmission shifting, braking, airbag deployment, and infotainment systems. The CAN network ensures these systems work together seamlessly by transmitting sensor data, commands, and status updates in real time. For example, the engine control module (ECM) can send vehicle speed information to the transmission control module (TCM), allowing for smooth gear shifts based on driving conditions.

How a CAN Network Works
The CAN bus operates using a differential signal over its two dedicated wires. Modules send messages using unique identifiers, ensuring priority data—such as safety-related commands—transmits without delay. When a module sends a message, every other module on the network receives it but only acts if the information is relevant to its function. The network constantly monitors data integrity, checking for errors to prevent corrupted messages from affecting vehicle performance.
Symptoms of a Faulty CAN Network
A malfunctioning CAN network can cause a variety of issues, ranging from minor glitches to critical failures. Some common signs of CAN network problems include:
- Multiple Warning Lights on the Dashboard: When the CAN network fails, modules may be unable to communicate, leading to erroneous warning lights such as ABS, airbag, or check engine indicators.
- Intermittent Electrical Issues: Malfunctions in vehicle systems, such as unresponsive instrument clusters, erratic power window behavior, or non-functional climate controls, may stem from CAN-related problems.
- Loss of Communication with a Module: If a single module fails, it may cause other modules to lose communication, leading to cascading failures.
- No-Start Condition: If critical modules like the ECM or immobilizer system cannot communicate, the vehicle may refuse to start.
- Unusual Behaviors in Vehicle Operation: Transmission shifting irregularities, ABS malfunctions, or sudden loss of power steering may result from CAN errors.
Common Causes of CAN Network Failures
- Damaged or Corroded CAN Wires: Physical damage, water intrusion, or corrosion can disrupt the signal integrity, leading to intermittent or total communication loss.
- Faulty Modules: A defective ECU may send incorrect signals or create excessive network traffic, interfering with proper communication.
- Short Circuits or Open Circuits: Electrical faults in the wiring can prevent proper data transmission, causing modules to become unresponsive.
The Importance of Proper CAN Network Diagnosis
Because so many vehicle functions depend on a healthy CAN network, diagnosing faults requires expert knowledge. Many repair attempts fail because a faulty module is misdiagnosed, or the root cause of the communication issue is overlooked. At XeMODeX, we understand the intricacies of CAN networks and use our specialized diagnostic equipment to pinpoint issues accurately. Our in-depth expertise ensures that repaired modules integrate seamlessly with the vehicle’s communication network, preventing recurring failures and unnecessary replacements.
Visit www.xemodex.com to check out our products and services.